Health
Dangerous Effects Of Sugar: How Sugar Kills Your Immune System, Causes Heart Diseases, Stroke, Cancer
The detrimental effects of sugar on body organs, such as the heart, brain, and vital systems, lead to severe health issues like heart disease, stroke, and cancer
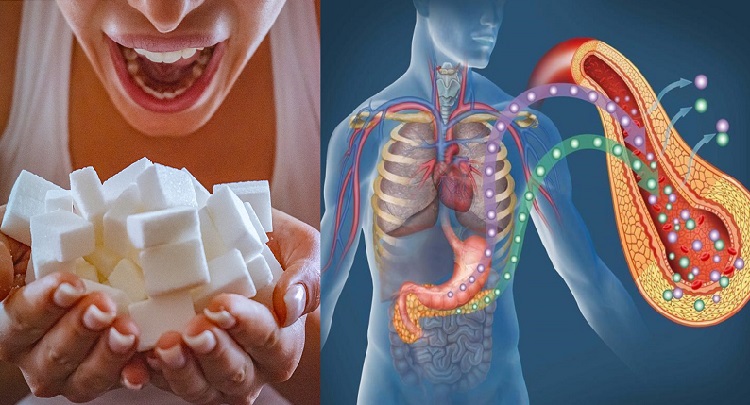
The detrimental effects of sugar on body organs, such as the heart, brain, and vital systems, lead to severe health issues like heart disease, stroke, and cancer
Excessive sugar intake can weaken the immune system by impairing immune cell function, promoting inflammation, and compromising gut health.
Sugar, once considered a harmless indulgence, is now recognized as a significant contributor to various health problems plaguing modern society. From obesity to diabetes, the excessive consumption of sugar has been linked to a myriad of dangerous effects on the human body.
In this article, we’ll explore how sugar affects different organs and immune systems within the body, shedding light on the importance of reducing sugar intake for overall health and well-being.
What’s the Effects of Sugar on Your Body?
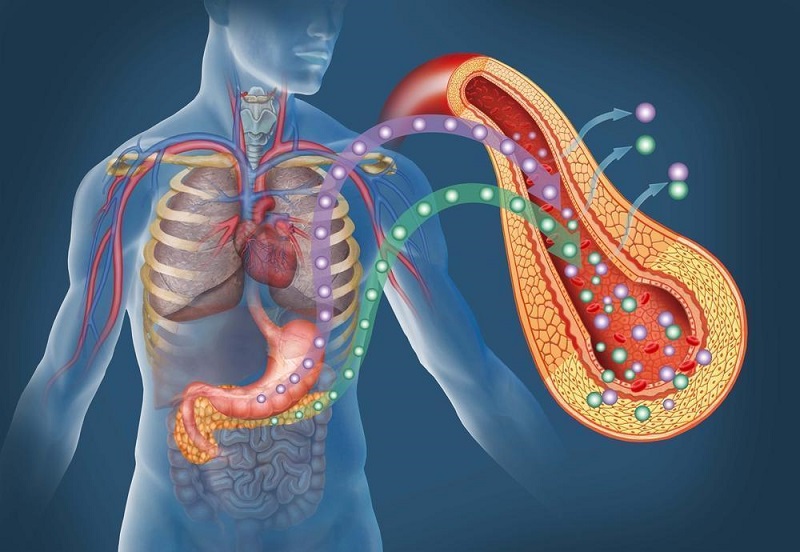
Sugar is a simple carbohydrate that is found in many foods, including fruits, vegetables, and grains. When consumed, it is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream and used as a source of energy by the body.
However, consuming too much sugar can have negative effects on the body. Our bodies thrive on a balanced diet, and although sugar can provide a burst of energy in the short term, it can be detrimental to your health in the long run.
Eating too much sugar causes spikes in our glucose levels, which can lead to insulin resistance and even put you at risk for type 2 diabetes. Consuming excessive amounts of added sugars also increases the risk of chronic diseases such as obesity and heart disease. Therefore, it is important to limit your intake of added sugars and focus on consuming foods that are naturally rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
How Sugar Destroys Immune System
Impaired Immune Response: Excessive sugar intake has been linked to weakened immune function. High levels of sugar in the bloodstream can impair the ability of white blood cells, which are crucial components of the immune system, to effectively combat pathogens such as bacteria and viruses.
This impairment can make individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
Increased Inflammation
Sugar consumption triggers inflammation within the body, which can negatively impact immune function. Chronic inflammation can disrupt the balance of immune cells and cytokines, leading to an overactive or dysregulated immune response.
This chronic low-grade inflammation can weaken the immune system’s ability to respond appropriately to pathogens and may contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases.
Here are the effects of sugar on the body immune system:
1. Reduced White Blood Cell Function
High sugar intake can impair the function of white blood cells, including neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes, which play key roles in immune defense. For example, studies have shown that high blood sugar levels can impair the ability of neutrophils to engulf and destroy bacteria, compromising the body’s ability to fight infections.
2. Increased Susceptibility to Infections
Diets high in sugar have been associated with an increased risk of infections, including respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, and gum disease. Elevated blood sugar levels can create a more hospitable environment for pathogens to thrive, making it easier for infections to take hold and spread within the body.
3. Compromised Gut Health
Sugar consumption can negatively impact gut health, which plays a critical role in immune function.
Diets high in sugar can disrupt the balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut microbiota, leading to dysbiosis and increased intestinal permeability (leaky gut). This disruption of gut homeostasis can impair immune function and increase susceptibility to infections and inflammatory conditions.
Dangerous Effects of Sugar on Body Organs
Blow are the dangerous effects of sugar in the human body:
1. Impact on Weight and Obesity (Weight Gain)
Sugar is dense in calories but low in essential nutrients, leading to excessive calorie consumption without providing necessary nutrients. Consuming sugary foods and drinks can contribute to weight gain and obesity over time.
This excess weight can increase the risk of other health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and certain cancers.
2. Effect on Blood Sugar Levels (Diabetes)
When you consume sugary foods or beverages, your blood sugar levels spike rapidly, leading to a surge in insulin production. Over time, this cycle of sugar highs and crashes can disrupt insulin sensitivity, leading to insulin resistance and eventually type 2 diabetes.
3. Contribution to Heart Disease
High sugar intake has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Excessive sugar consumption can raise blood pressure, increase triglyceride levels, and promote inflammation within the body, all of which are risk factors for heart disease.
4. Liver Damage
The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing sugar. When you consume too much sugar, the liver becomes overwhelmed and starts converting excess sugar into fat, which can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and eventually progress to more severe liver conditions such as cirrhosis.
5. Impact on Brain Health
Research suggests that excessive sugar consumption may have negative effects on cognitive function and mental health. High sugar diets have been linked to an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline.
Additionally, sugar consumption can impair memory and learning abilities.
6. Promotion of Inflammation
Sugar consumption triggers inflammation within the body, which is associated with various chronic diseases such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and certain types of cancer. Chronic inflammation can also exacerbate existing health conditions and impair overall immune function.
In conclusion, the dangerous effects of sugar on the human body cannot be overstated. From weight gain and obesity to heart disease and liver damage, excessive sugar consumption can wreak havoc on multiple organs and systems within the body. T
To safeguard your health, it’s essential to be mindful of your sugar intake and opt for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible. By making small but meaningful changes to your diet and lifestyle, you can reduce your risk of developing sugar-related health problems and enjoy better overall health and well-being.
























You must be logged in to post a comment Login